The notion of the value chain was first presented by Harvard Business School professor Michael E Porter. The value chain encompasses the whole spectrum of actions required in getting a product to market and the ultimate customer, from start to finish. These steps add value to the product, from raw materials to marketing, sales, and after-sales support.
A value chain analysis examines all of these processes for a firm and how they contribute to the product’s value—a value chain analysis aids in the optimization of these operations for better results. Companies can not only save money by optimizing their value chains, but they can also enhance their operational efficiency. This type of optimization increases efficiency and can provide a competitive edge. This is a breakdown of Apple Inc.’s value chain.
Apple’s Value Chain Analysis
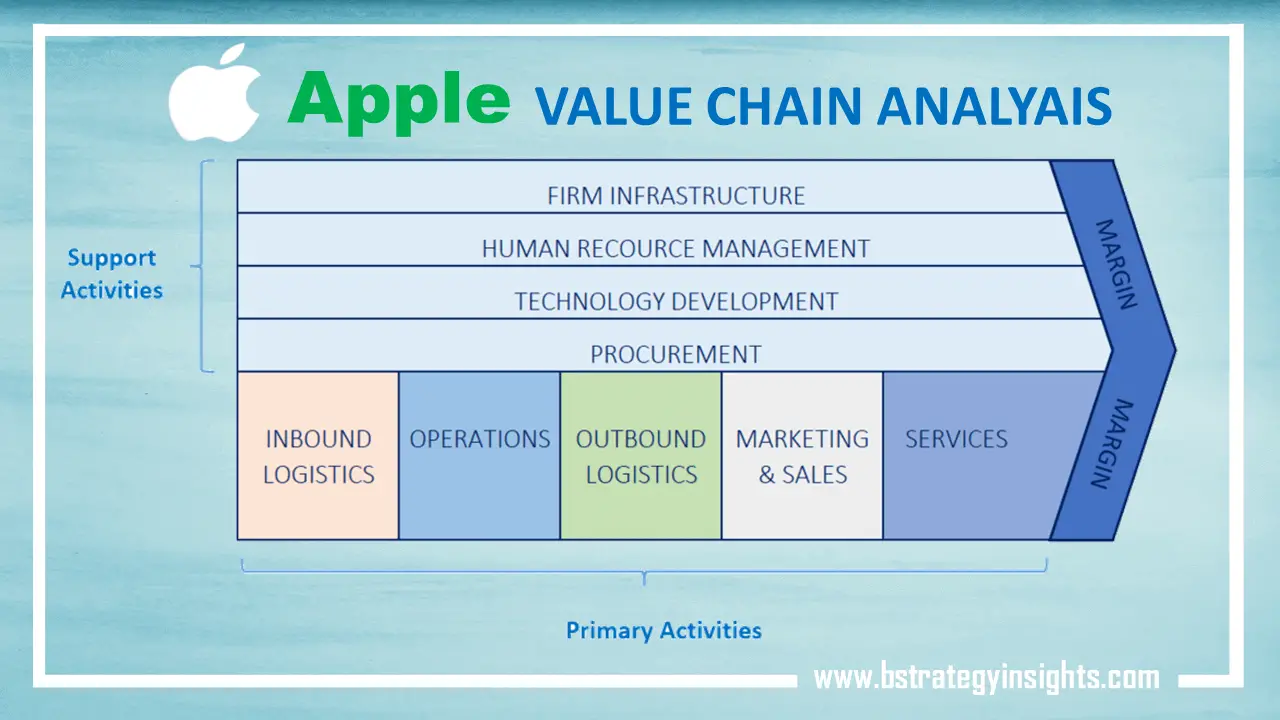
The value chain is divided into two types of activities: main and support activities. Both are mentioned farther down:
Primary activities
Apple’s Inbound logistics
Apple has a massive supply chain, and it has several alternatives to getting raw materials. Its top 200 suppliers include component suppliers and others who accounted for at least 97 percent of its materials, manufacturing, and assembly procurement spending in 2016.
China and Japan are home to a substantial number of the company’s leading suppliers. 3M and Foxconn are two of its key raw material suppliers. Apple has a lot of negotiating leverage with its suppliers because of its financial heft. It has set quality requirements for its suppliers to ensure that its goods and services meet the highest possible standards. Apart from that, Apple has used more sophisticated ways to decrease storage needs and expedite the purchase process.
Apple’s Operations
Apple goods are manufactured in several different countries. However, most of its items are assembled in China, which is why some of them have the Made in China label. Apple is also in negotiations with the Indian government, and production might begin there shortly.
A significant portion of the assembly is done in China, although a minor part is done in other countries. Because labor expenses are lower in Asian countries, Apple’s production costs are cheaper. Aside from that, Apple has decreased the usage of hazardous chemicals in its product production and assembly. Apple is increasingly using recyclable materials. By outsourcing its production, on the other hand, the company has been able to control its production costs to an acceptable level.
Apple’s Outbound logistics
Apple has a massive distribution network that includes both direct and indirect channels. Apple has an extensive channel for distributing its products to clients, ranging from retail shops to internet shopping and its own branded stores. It has improved its distribution route and increased the number of brand outlets over time. Apart from these considerations, the focus has remained on green packaging and waste reduction.
Apple’s Marketing and sales
Apple is a well-known brand whose goods are recognized for their high quality, innovative design, and technical advancements. Any new Apple product is news, and it is covered not only by the media but also by a variety of other sources, including small and large websites. That does not, however, imply that Apple does not invest in brand marketing.
While Apple’s goods are extensively promoted in the media, it also creates distinctive advertisements that engage its fans. It has a high level of brand loyalty due to its advertising strategy’s originality and imagination. Apart from television and internet commercials, the company also uses print advertisements to market and promote its products.
Apple sells its products through the following channels:
- Value-added resellers
- Retailers
- Wholesalers
- Third-party cellular network carriers
- Direct salesforce
- Apple online store
- Apple retail stores
The IT behemoth is steadily expanding the proportion of sales made through direct channels instead of indirect ones. Net sales through the company’s direct and indirect distribution channels will account for 34 percent and 66 percent of total net sales in 2020, respectively. Apple has been focusing more on corporate sales in recent years, and CEO Tim Cook recently indicated that the company would rely heavily on channel partners to boost enterprise sales even more.
Apple’s Products and services
Apple provides its customers with complete after-sales assistance. The majority of Apple goods come with 90 days of free service and a one-year limited warranty. Aside from that, Apple users may get support via the online shop. They may monitor the status of their order online. Customers may talk to professionals online or call Apple for assistance. Customers may fix their phones or other Apple goods at an Apple-approved service provider or an Apple shop with a genius bar.
Apple provides outstanding customer support at all three phases of the buying process: pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase. Apple has experience centers in key cities worldwide where anybody may try out its goods and get persuaded of their excellence. Apple salespeople are often well-trained, courteous young men and women tech-savvy and eager to show product features and capabilities.
With unique iPhone trade-in schemes that allow iPhone customers to switch to newer models with additional cost, post-purchase customer care is also outstanding. Only products purchased directly from Apple, either online or at an Apple Retail Store, can be returned to Apple. Within 14 calendar days of purchase, products can be returned.
Customers can go to Apple Stores if they are unsure about anything or if something goes wrong. Customers have had their broken iPhone screens fixed for free at an Apple Store in the past.
Support activities
Apple’s Technology/Research and development
Apple invests a lot of money in R&D. Its brand is recognized for technical innovation as well as high quality and distinctive product designs. The brand must invest heavily in R&D in order to preserve its competitive advantage.
The company spent more than ten billion dollars on research and development in 2016 and 11.6 billion dollars in 2017. Apple has raised its R&D investment by more than 5 billion dollars since 2014. Three significant causes fuel this drive. Its expanded product variety, increasing the scope of Apple’s services, and increased concentration on in-house technological development are among them.
Apple’s Human Resource Management
Human resource management is also an essential element of a company’s value chain. Apple prioritizes both hiring and remuneration. Since the days of Apple founder Steve Jobs, this has been the standard. Apple has always sought the most acceptable candidates. However, during Tim Cook’s tenure, the HRM style has shifted slightly. Apart from inclusion and diversity, the new CEO has implemented many measures to improve Apple’s HR reputation.
Apple’s Procurement
At Apple, procurement is also a significant priority. It has maintained positive ties with its vendors. Suppliers must provide safe working conditions for employees as well as goods and services that meet industry standards. All of these variables have an impact on supplier relationships. Apple, on the other hand, is a big buyer for most of its suppliers. Thus the two have a mutually beneficial partnership.
Apple’s Firm Infrastructure
The infrastructure of every organization plays a critical role in its success. The infrastructure of any company includes everything from management to financial and other resources and culture and organization. The better a company’s infrastructure is managed, the greater its capacity to generate revenues. Apple, for example, has just undergone a massive cultural shift.
Conclusion
Apple can choose and acquire high-grade raw material and create customer loyalty based on Value Chain Analysis. Value Chain Analysis may also be used to establish brand identity. Apple may potentially get a competitive advantage by accelerating the delivery of offered items to end-users.