What is Value Chain Analysis?
Value chain analysis is a technique used to analyze the business activities of a company to determine how it achieves a competitive advantage. The value chain analysis of a company helps it understand how it adds value or what its customers appreciate about it. Through value chain analysis, a company can identify processes that generate more revenues and profit and how it can sell its products for a margin that covers the cost of adding the value to them.
A company that has an efficient value chain should not have a problem in generating profits. It is because it can provide more value for its customers than the cost it takes to make its products or services. For the efficient value chain, its customers will also return frequently and prefer its products or services over its competitors.
The value chain analysis first came forward in the 1980s by Michael Porter. Therefore, another name used for value chain analysis is Porter’s Value Chain Analysis. The basis for the value chain analysis is value-addition in the form of a value chain. Porter suggested that there are two types of activities in an organization, primary and support. He also stated that a company has five primary activities and four support activities.
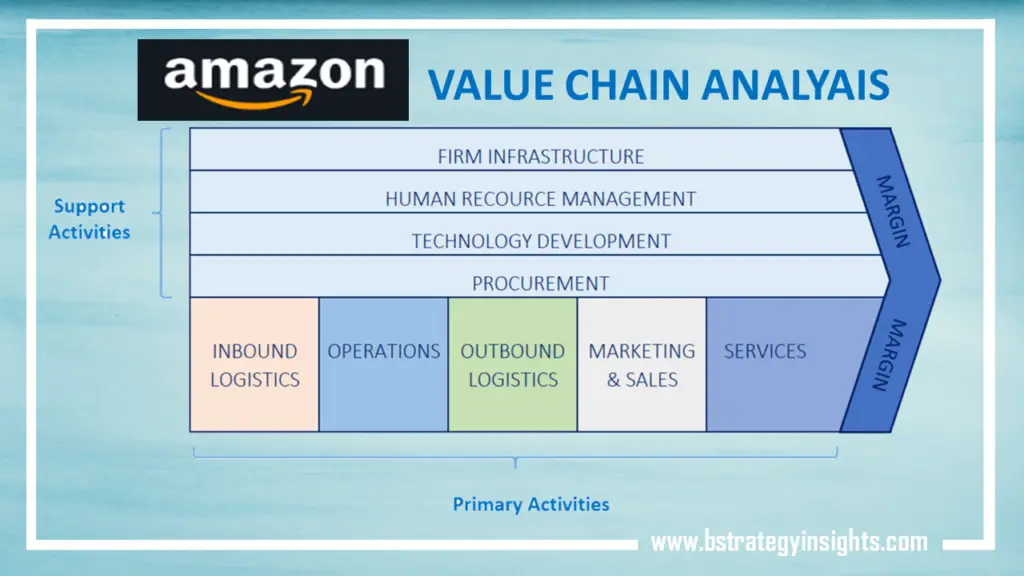
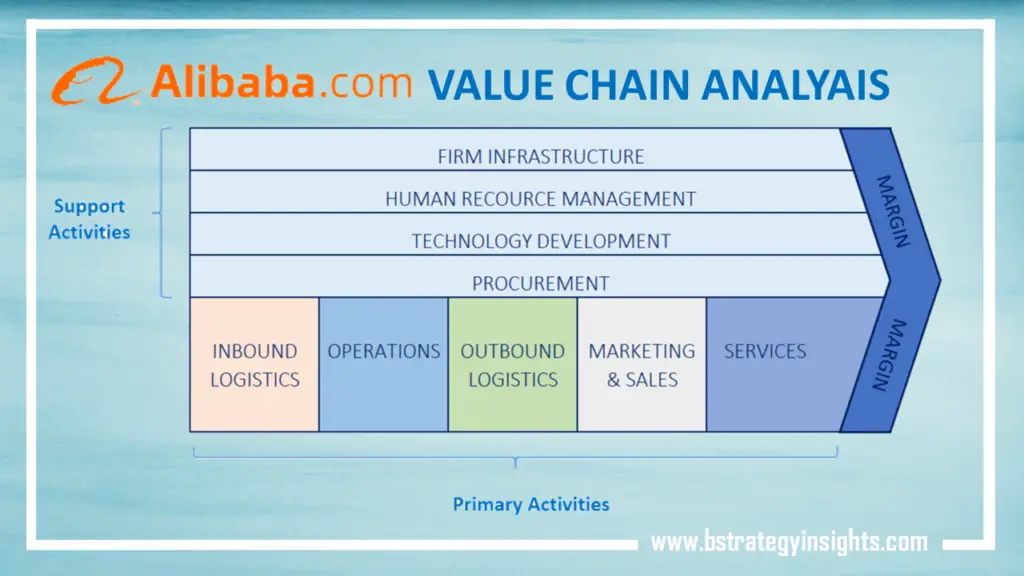
Below is the Port’s value chain analysis diagram:
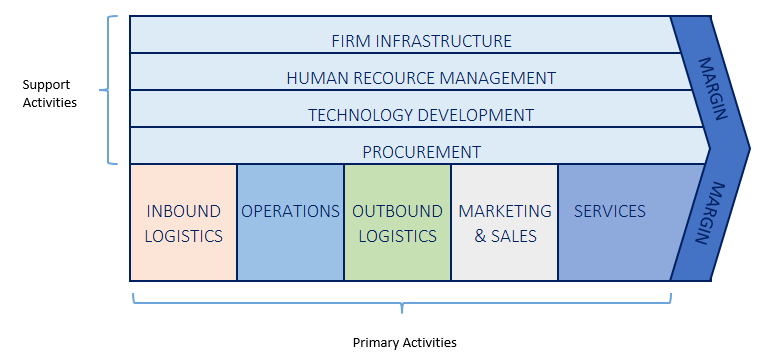
Porter suggested that all activities within an organization add value to its products or services and, therefore, both primary and support activities play a vital role in achieving a competitive edge for a company. However, Porter also suggested that all these activities should run at an optimum level for a company to gain any real competitive advantage.
The value chain analysis also complements another model developed by Porter known as Generic Strategies. Porter suggested that for a company to achieve a competitive advantage, it must put a generic strategy into practice, which includes Cost Leadership, Differentiation, or Focus. The competitive advantage of a company is linked directly to what activities it undertakes.
What is Value and Value Chain?
Value refers to the amount that customers are willing to pay for the products and services of a company. In simpler words, it represents the price of a product or service that customers for which customers will pay the company. When the value of a product or service exceeds its costs, it generates a margin, or in simpler words, a profit.
In the model, margin implies that companies realize profit margin that depends on their ability to cooperate their primary and support activities in their value chain. In other words, by efficiently linking and synchronizing their primary and support activities, companies can make products or services for which customers will pay value.
A company’s value chain concentrates on the activities starting from how it obtains raw materials to their subsequent conversion into finished products or services and eventual sale to customers. The source of a company’s competitive edge comes from its discrete activities and how these activities interact with each other. The goal of a company in performing value chain analysis, therefore, is to create value while controlling costs.
What are the concepts of Value Chain Analysis?
As mentioned, value chain analysis consists of analyzing the primary and support activities of a company. Most companies have various activities in the process of converting its inputs into outputs. These are the products that go under either primary or support activities.
Primary activities
Primary activities represent activities concerned with creating and delivering products or services. According to Porter, there are five primary activities in a company’s value chain namely inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
Inbound logistics
Inbound logistics of a company represents the processes involved in receiving goods from suppliers. Apart from receiving these goods, inbound logistics also include storing and handling those goods. The inbound logistics of a company represent activities that initiate its value chain processes. For example, a company can determine an optimum level of raw materials to decrease its costs in this process.
Operations
Operations, in the value chain analysis model, show the processes involved in converting the raw materials of a company into finished goods. A company can add value to this process as the raw material move into the next stage. For example, a company can use machinery or skilled workers to add quality to their products.
Outbound logistics
Outbound logistics comes after the conversion process of raw materials. It includes storing, distributing, and delivering finished goods to customers. Companies can also add value to this process and achieve a competitive advantage. For example, a company can reduce its delivery times for customers to prefer its products over competitors.
Marketing and sales
Marketing and sales are processes that are not related to the raw materials or finished goods of a company. Through marketing, a company can ensure that its products target the correct customer group. Similarly, in this process, companies can develop a marketing mix to gain a competitive edge. For example, a company can advertise its products to reach a wider audience.
Service
The primary activities of a company don’t only relate to obtaining and delivering goods to customers. It also involves what comes afterward. Service, in value chain analysis, refers to activities that occur after a company sells its products, such as installation, training, repair, customer services, etc. For example, a company can focus on providing quality customer services to achieve a competitive advantage.
Support activities
Support activities refer to activities that enhance the primary activities and help a company achieve a competitive advantage. There are four support activities, as suggested by Porter. These are firm infrastructure, technological development, human resources management, and procurement.
Firm infrastructure
Firm infrastructure refers to the organization of a company. It includes processes such as accounting, legal, and management structure of a company. If a company wants to achieve a competitive advantage, it must ensure its firm infrastructure supports in primary activities. For example, a company can focus on planning to achieve its goals better.
Technology development
Technology development is a support activity that relates to how a company uses technology to achieve a competitive advantage. In the modern world, most companies have used technology to reach a wider audience while also focusing on their primary activities. For example, a company can make a website through which it can allow customers to place orders.
Human resources management
Human resources management refers to the idea that a company must invest in its workforce. For instance, they can recruit, train, and develop their employees to achieve better results. It also involves motivating the workforce. In many industries, human resources management is more crucial compared to others. For example, a company can train its employees to support its primary activities.
Procurement
Lastly, procurement is the process that comes before inbound logistics. If a company cannot excel in procurement, it cannot achieve value in its other activities. Procurement refers to the process of obtaining raw materials for the best price possible. For example, a company can get discounts or buy better quality products to support its activities.
Why is Value Chain Analysis important?
Value chain analysis is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, It allows a company to analyze its primary and support activities and identify any processes that need improvements. Similarly, it helps the company develop better products or services to obtain a competitive advantage. It, in turn, helps the company increase its revenues and profits.
Value chain analysis also helps in standardizing the process of a company by providing them with a benchmark against which it can compare its performance. Most importantly, it allows companies to reduce their costs to achieve better value for which customers will be willing to pay. It can also help in determining a price that customers can pay.
Furthermore, value chain analysis allows companies to improve the flow of materials and products through better value chain management. Likewise, it can help enhance the after-sale services provided to customers, especially customer support, which most customers value in the modern world. The value chain analysis can also help in identifying technological developments that companies can use to achieve a competitive advantage.
Companies can also perform a value chain analysis of their competitors or similar companies to gain valuable insights into what customers want. By comparing their value chain with their competitors, companies can identify areas in which they can generate a competitive advantage over those competitors. Therefore, the value chain analysis is also an outstanding comparison tool for companies.
Overall, the value chain analysis allows companies to identify the processes that add value to their products or services. It can result in a better analysis of what customers prefer and how they can stay loyal. It is a powerful tool in identifying all the processes in a company that needs improvement or focus.
Conclusion
Value chain analysis is a technique commonly used in analyzing the activities of a company to determine which ones add value. Through this analysis, companies can increase their competitive advantage. The value chain analysis divides a company’s activities into two categories, primary, and support. The model suggests a company has five primary and four support activities that must work together in order to generate a margin for its products and services.